[ English | Indonesia | русский ]
Ceph 生产示例¶
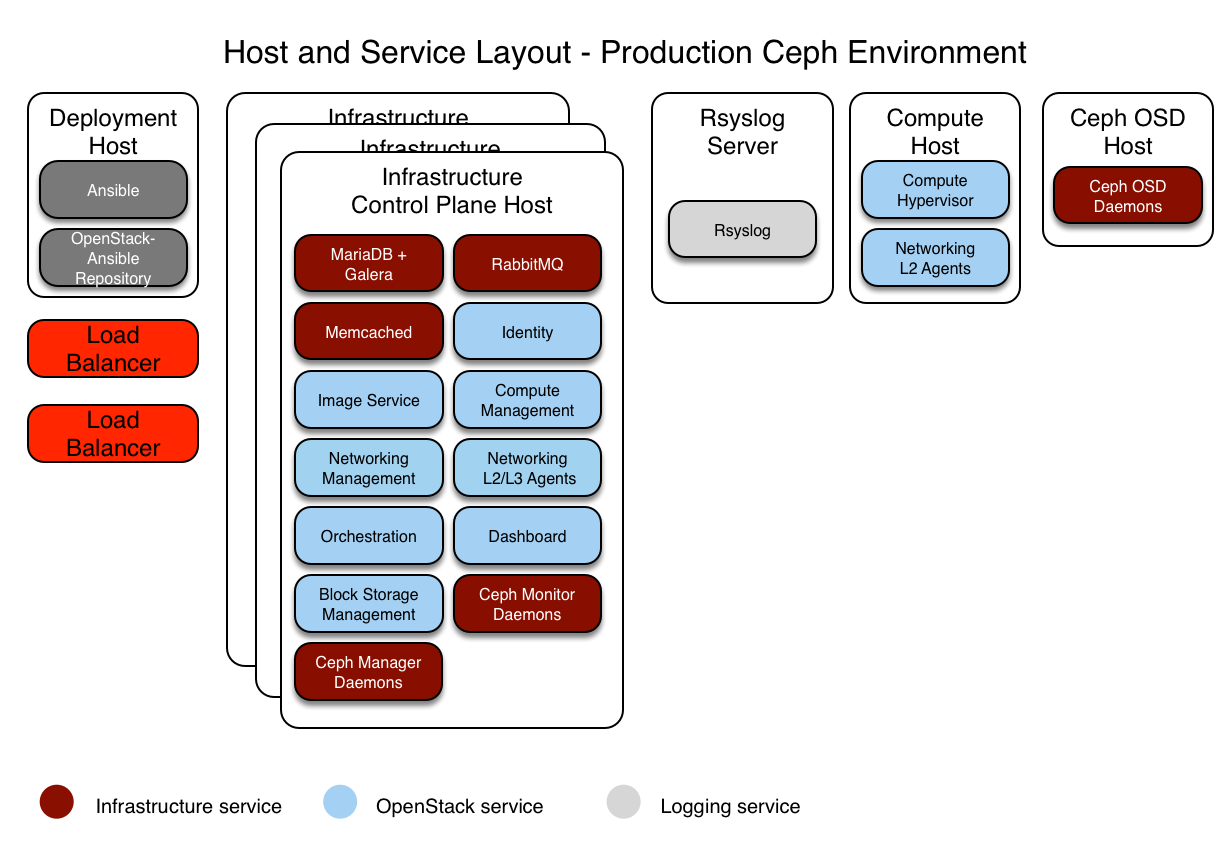
本节描述了一个使用高可用性服务和 Ceph 后端来存储镜像、卷和实例的 OpenStack-Ansible (OSA) 部署的生产环境示例。
此示例环境具有以下特性
三个基础设施(控制平面)主机,带有 ceph-mon 容器
两个计算主机
三个 Ceph OSD 存储主机
一个日志聚合主机
每个主机配置了多个网络接口卡 (NIC) 作为绑定对
完整的计算套件,包含遥测服务 (ceilometer),并配置 Ceph 作为镜像 (glance) 和块存储 (cinder) 服务的存储后端
通过路由器地址 172.29.236.1 在管理网络上访问互联网
与 Ceph 的集成¶
OpenStack-Ansible 允许以三种方式集成 Ceph 存储 集群
通过指向其信息在
user_variables.yml中连接到您自己预部署的 Ceph 集群,并允许 OpenStack-Ansible 通过 ssh 连接到 Ceph 监控器以检索 ceph.conf 和密钥环的内容。此方法只需要在
user_variables.yml中进行少量配置,以指向外部 Ceph 集群监控器。 Ceph-Ansible 的所有配置都将位于 OpenStack-Ansible 部署之外,并且不会重复。ceph_mons变量需要一个 Ceph 监控服务器的 IP 地址列表,这些服务器位于外部 Ceph 部署中
注意
只有在使用未在 OpenStack-Ansible 的清单中存在的外部集群(即未定义 mon_group_name 组)时,才需要覆盖 ceph_mons。
ceph_mons:
- 172.29.244.151
- 172.29.244.152
- 172.29.244.153
通过指向
user_variables.yml中的监控器(如上所述)连接到您自己预部署的 Ceph 集群,并提供数据以填充部署主机上的 ceph.conf 和 ceph 密钥环文件。 这在 此处 进行了描述。 OpenStack-Ansible 不需要通过 ssh 访问 Ceph 集群。通过使用 Ceph-Ansible 项目维护的角色,将 Ceph 集群作为 OpenStack-Ansible 部署的一部分进行部署。 部署者可以通过将主机添加到
openstack_user_config.yml中的ceph-mon_hosts和ceph-osd_hosts组中来启用ceph-install.ymlplaybook。 为了启用ceph-rgw-install.ymlplaybook,您需要在openstack_user_config.yml中添加ceph-rgw_hosts。
注意
请注意,RGW 安装应在部署 Keystone 服务之后进行。
一旦定义了组,您就可以在 OpenStack-Ansible 的 user_variables.yml 文件中配置 Ceph-Ansible 特定变量。
警告
不建议将 Ceph 集群作为 OpenStack-Ansible 的一部分进行部署,因为 Ceph-Ansible 的升级路径未经测试或支持。 此选项主要用于 CI 和 AIO 部署,以测试和演示软件堆栈的示例集成。
本示例将重点介绍 OpenStack-Ansible 及其 Ceph 集群的部署。
网络配置¶
网络 CIDR/VLAN 分配¶
此环境使用以下 CIDR 和 VLAN 分配。
网络 |
CIDR |
VLAN |
|---|---|---|
管理网络 |
172.29.236.0/22 |
10 |
隧道 (VXLAN) 网络 |
172.29.240.0/22 |
30 |
存储网络 |
172.29.244.0/22 |
20 |
IP 分配¶
此环境使用以下主机名和 IP 地址分配。
主机名 |
管理 IP |
隧道 (VXLAN) IP |
存储 IP |
|---|---|---|---|
lb_vip_address |
172.29.236.9 |
||
infra1 |
172.29.236.11 |
172.29.240.11 |
|
infra2 |
172.29.236.12 |
172.29.240.12 |
|
infra3 |
172.29.236.13 |
172.29.240.13 |
|
log1 |
172.29.236.14 |
||
compute1 |
172.29.236.16 |
172.29.240.16 |
172.29.244.16 |
compute2 |
172.29.236.17 |
172.29.240.17 |
172.29.244.17 |
osd1 |
172.29.236.18 |
172.29.244.18 |
|
osd2 |
172.29.236.19 |
172.29.244.19 |
|
osd3 |
172.29.236.20 |
172.29.244.20 |
主机网络配置¶
每个主机都需要实现正确的网络桥接。以下是 infra1 的 /etc/network/interfaces 文件。
注意
如果您的环境没有 eth0,而是有 p1p1 或其他接口名称,请确保将所有配置文件中的所有对 eth0 的引用替换为适当的名称。 同样适用于其他网络接口。
# This is a multi-NIC bonded configuration to implement the required bridges
# for OpenStack-Ansible. This illustrates the configuration of the first
# Infrastructure host and the IP addresses assigned should be adapted
# for implementation on the other hosts.
#
# After implementing this configuration, the host will need to be
# rebooted.
# Assuming that eth0/1 and eth2/3 are dual port NIC's we pair
# eth0 with eth2 and eth1 with eth3 for increased resiliency
# in the case of one interface card failing.
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet manual
bond-master bond0
bond-primary eth0
auto eth1
iface eth1 inet manual
bond-master bond1
bond-primary eth1
auto eth2
iface eth2 inet manual
bond-master bond0
auto eth3
iface eth3 inet manual
bond-master bond1
# Create a bonded interface. Note that the "bond-slaves" is set to none. This
# is because the bond-master has already been set in the raw interfaces for
# the new bond0.
auto bond0
iface bond0 inet manual
bond-slaves none
bond-mode active-backup
bond-miimon 100
bond-downdelay 200
bond-updelay 200
# This bond will carry VLAN and VXLAN traffic to ensure isolation from
# control plane traffic on bond0.
auto bond1
iface bond1 inet manual
bond-slaves none
bond-mode active-backup
bond-miimon 100
bond-downdelay 250
bond-updelay 250
# Container/Host management VLAN interface
auto bond0.10
iface bond0.10 inet manual
vlan-raw-device bond0
# OpenStack Networking VXLAN (tunnel/overlay) VLAN interface
auto bond1.30
iface bond1.30 inet manual
vlan-raw-device bond1
# Storage network VLAN interface (optional)
auto bond0.20
iface bond0.20 inet manual
vlan-raw-device bond0
# Container/Host management bridge
auto br-mgmt
iface br-mgmt inet static
bridge_stp off
bridge_waitport 0
bridge_fd 0
bridge_ports bond0.10
address 172.29.236.11
netmask 255.255.252.0
gateway 172.29.236.1
dns-nameservers 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4
# OpenStack Networking VXLAN (tunnel/overlay) bridge
#
# The COMPUTE, NETWORK and INFRA nodes must have an IP address
# on this bridge.
#
auto br-vxlan
iface br-vxlan inet static
bridge_stp off
bridge_waitport 0
bridge_fd 0
bridge_ports bond1.30
address 172.29.240.16
netmask 255.255.252.0
# OpenStack Networking VLAN bridge
auto br-vlan
iface br-vlan inet manual
bridge_stp off
bridge_waitport 0
bridge_fd 0
bridge_ports bond1
# compute1 Network VLAN bridge
#auto br-vlan
#iface br-vlan inet manual
# bridge_stp off
# bridge_waitport 0
# bridge_fd 0
#
# For tenant vlan support, create a veth pair to be used when the neutron
# agent is not containerized on the compute hosts. 'eth12' is the value used on
# the host_bind_override parameter of the br-vlan network section of the
# openstack_user_config example file. The veth peer name must match the value
# specified on the host_bind_override parameter.
#
# When the neutron agent is containerized it will use the container_interface
# value of the br-vlan network, which is also the same 'eth12' value.
#
# Create veth pair, do not abort if already exists
# pre-up ip link add br-vlan-veth type veth peer name eth12 || true
# Set both ends UP
# pre-up ip link set br-vlan-veth up
# pre-up ip link set eth12 up
# Delete veth pair on DOWN
# post-down ip link del br-vlan-veth || true
# bridge_ports bond1 br-vlan-veth
# Storage bridge (optional)
#
# Only the COMPUTE and STORAGE nodes must have an IP address
# on this bridge. When used by infrastructure nodes, the
# IP addresses are assigned to containers which use this
# bridge.
#
auto br-storage
iface br-storage inet manual
bridge_stp off
bridge_waitport 0
bridge_fd 0
bridge_ports bond0.20
# compute1 Storage bridge
#auto br-storage
#iface br-storage inet static
# bridge_stp off
# bridge_waitport 0
# bridge_fd 0
# bridge_ports bond0.20
# address 172.29.244.16
# netmask 255.255.252.0
部署配置¶
环境布局¶
/etc/openstack_deploy/openstack_user_config.yml 文件定义了环境布局。
以下配置描述了此环境的布局。
---
cidr_networks: &cidr_networks
management: 172.29.236.0/22
tunnel: 172.29.240.0/22
storage: 172.29.244.0/22
used_ips:
- "172.29.236.1,172.29.236.50"
- "172.29.240.1,172.29.240.50"
- "172.29.244.1,172.29.244.50"
- "172.29.248.1,172.29.248.50"
global_overrides:
cidr_networks: *cidr_networks
internal_lb_vip_address: 172.29.236.9
#
# The below domain name must resolve to an IP address
# in the CIDR specified in haproxy_keepalived_external_vip_cidr.
# If using different protocols (https/http) for the public/internal
# endpoints the two addresses must be different.
#
external_lb_vip_address: openstack.example.com
management_bridge: "br-mgmt"
provider_networks:
- network:
container_bridge: "br-mgmt"
container_type: "veth"
container_interface: "eth1"
ip_from_q: "management"
type: "raw"
group_binds:
- all_containers
- hosts
is_management_address: true
- network:
container_bridge: "br-vxlan"
container_type: "veth"
container_interface: "eth10"
ip_from_q: "tunnel"
type: "vxlan"
range: "1:1000"
net_name: "vxlan"
group_binds:
- neutron_openvswitch_agent
- network:
container_bridge: "br-vlan"
container_type: "veth"
container_interface: "eth12"
host_bind_override: "eth12"
type: "flat"
net_name: "physnet1"
group_binds:
- neutron_openvswitch_agent
- network:
container_bridge: "br-vlan"
container_type: "veth"
container_interface: "eth11"
type: "vlan"
range: "101:200,301:400"
net_name: "physnet2"
group_binds:
- neutron_openvswitch_agent
- network:
container_bridge: "br-storage"
container_type: "veth"
container_interface: "eth2"
ip_from_q: "storage"
type: "raw"
group_binds:
- glance_api
- cinder_api
- cinder_volume
- manila_share
- nova_compute
- ceph-mon
- ceph-osd
###
### Infrastructure
###
_infrastructure_hosts: &infrastructure_hosts
infra1:
ip: 172.29.236.11
infra2:
ip: 172.29.236.12
infra3:
ip: 172.29.236.13
# nova hypervisors
compute_hosts: &compute_hosts
compute1:
ip: 172.29.236.16
compute2:
ip: 172.29.236.17
ceph-osd_hosts:
osd1:
ip: 172.29.236.18
osd2:
ip: 172.29.236.19
osd3:
ip: 172.29.236.20
# galera, memcache, rabbitmq, utility
shared-infra_hosts: *infrastructure_hosts
# zookeeper
coordination_hosts: *infrastructure_hosts
# ceph-mon containers
ceph-mon_hosts: *infrastructure_hosts
# ceph-mds containers
ceph-mds_hosts: *infrastructure_hosts
# ganesha-nfs hosts
ceph-nfs_hosts: *infrastructure_hosts
# repository (apt cache, python packages, etc)
repo-infra_hosts: *infrastructure_hosts
# load balancer
# Ideally the load balancer should not use the Infrastructure hosts.
# Dedicated hardware is best for improved performance and security.
load_balancer_hosts: *infrastructure_hosts
###
### OpenStack
###
# keystone
identity_hosts: *infrastructure_hosts
# cinder api services
storage-infra_hosts: *infrastructure_hosts
# cinder volume hosts (Ceph RBD-backed)
storage_hosts: *infrastructure_hosts
# glance
image_hosts: *infrastructure_hosts
# placement
placement-infra_hosts: *infrastructure_hosts
# nova api, conductor, etc services
compute-infra_hosts: *infrastructure_hosts
# heat
orchestration_hosts: *infrastructure_hosts
# horizon
dashboard_hosts: *infrastructure_hosts
# neutron server, agents (L3, etc)
network_hosts: *infrastructure_hosts
# ceilometer (telemetry data collection)
metering-infra_hosts: *infrastructure_hosts
# aodh (telemetry alarm service)
metering-alarm_hosts: *infrastructure_hosts
# gnocchi (telemetry metrics storage)
metrics_hosts: *infrastructure_hosts
# manila (share service)
manila-infra_hosts: *infrastructure_hosts
manila-data_hosts: *infrastructure_hosts
# ceilometer compute agent (telemetry data collection)
metering-compute_hosts: *compute_hosts
环境定制¶
/etc/openstack_deploy/env.d 中的可选部署文件允许定制 Ansible 组。这允许部署者设置服务是在容器中运行(默认),还是在主机上运行(裸机)。
对于 Ceph 环境,您可以在容器中运行 cinder-volume。 为此,您需要在 /etc/openstack_deploy/env.d/cinder.yml 文件中创建以下内容
---
# This file contains an example to show how to set
# the cinder-volume service to run in a container.
#
# Important note:
# When using LVM or any iSCSI-based cinder backends, such as NetApp with
# iSCSI protocol, the cinder-volume service *must* run on metal.
# Reference: https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/lxc/+bug/1226855
container_skel:
cinder_volumes_container:
properties:
is_metal: false
用户变量¶
/etc/openstack_deploy/user_variables.yml 文件定义了默认变量的全局覆盖。
对于此示例环境,我们配置了一个 HA 负载均衡器。 我们在基础设施主机上使用 HA 层 (Keepalived) 实现负载均衡器 (HAProxy)。 您的 /etc/openstack_deploy/user_variables.yml 必须具有以下内容才能配置 HAProxy、Keepalived 和 Ceph
---
# Because we have three haproxy nodes, we need
# to one active LB IP, and we use keepalived for that.
# These variables must be defined when external_lb_vip_address or
# internal_lb_vip_address is set to FQDN.
## Load Balancer Configuration (haproxy/keepalived)
haproxy_keepalived_external_vip_cidr: "<external_ip_address>/<netmask>"
haproxy_keepalived_internal_vip_cidr: "172.29.236.9/32"
haproxy_keepalived_external_interface: ens2
haproxy_keepalived_internal_interface: br-mgmt
## Ceph cluster fsid (must be generated before first run)
## Generate a uuid using: python -c 'import uuid; print(str(uuid.uuid4()))'
generate_fsid: false
fsid: 116f14c4-7fe1-40e4-94eb-9240b63de5c1 # Replace with your generated UUID
## ceph-ansible settings
## See https://github.com/ceph/ceph-ansible/tree/2025.2/group_vars for
## additional configuration options available.
monitor_address_block: "{{ cidr_networks.storage }}"
public_network: "{{ cidr_networks.storage }}"
cluster_network: "{{ cidr_networks.storage }}"
journal_size: 10240 # size in MB
# ceph-ansible automatically creates pools & keys for OpenStack services
openstack_config: true
cinder_ceph_client: cinder
glance_ceph_client: glance
glance_default_store: rbd
glance_rbd_store_pool: images
nova_libvirt_images_rbd_pool: vms
cinder_backends:
rbd_volumes:
volume_driver: cinder.volume.drivers.rbd.RBDDriver
rbd_pool: volumes
rbd_ceph_conf: /etc/ceph/ceph.conf
rbd_store_chunk_size: 8
volume_backend_name: rbddriver
rbd_user: "{{ cinder_ceph_client }}"
rbd_secret_uuid: "{{ cinder_ceph_client_uuid }}"
report_discard_supported: true
